The following is the classification of Obesity, and how it is treated:
| BMI | Category | Health Risk | Suggested Treatment |
|---|
| 23 to 27.4 | Overweight | Moderate | Diet and Exercise |
| 27.4 to 32.4 | Obese | High | |
| 32.5 to 37.4 | Severely Obese | Very High | Consider Obesity
surgery
|
| 37.5 and above | Morbidly Obese | Very High | |
*BMI values for Asian population according to MOH guideline NIH Concensus Conference.
Dietary management
You can lose weight as long as you eat healthy. Have a doctor assess your diet patterns and suggest modifications to keep the weight under control.
Exercise/Physical therapy
Coupled with dietary changes, exercise offers the most effective approach for weight loss. A physiotherapist can prescribe exercise routines to meet your specific requirements.
Behaviour modification
Lifestyle changes play an important role in your fight against Obesity.
A behavioural therapist can recommend changes necessary to sustain a healthy lifestyle and achieve long-term weight loss.
Medical therapy
Have a doctor check for possible underlying causes of Obesity, and prescribe suitable medical treatment.
Surgery
with a BMI greater than 32.5 are advised to consider surgery for Obesity (also referred as "Bariatric Surgery") when all other treatment options have been unsuccessful. Surgery enables you to successfully lose weight and treat Obesity-related diseases. It also helps to sustain your weight loss for years, thus improving overall quality of life.
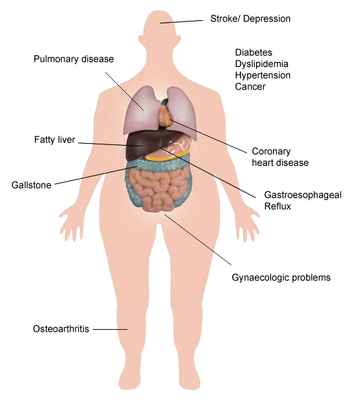
Surgery has proven to be an effective treatment for patients who are morbidly or severely obese for the last four decades. It is in fact backed up by a recent study of more than 22,000 patients that patients could expect to lose more than 60%* of their excess weight after bariatric surgery. Another study showed that following surgery, up to 80%* of patients experienced complete resolution or improvement of their co-morbid conditions, such as diabetes, hypertension and sleep apnoea.
In the last 10 years, with the "keyhole" or minimally invasive surgery, bariatric surgery has become much less invasive than the conventional surgery. It usually involves a modification of the digestive tract with the aim of reducing the size of gastric reservoir with or without reducing the ability of the gut to absorb food.