Sepsis Value-Driven Outcomes (VDO) in National University Hospital (NUH)
Case study
Background
- Community-acquired sepsis incurs high morbidity and mortality
- In 2019, there were 1,985 cases of sepsis in NUH, resulting in inpatient mortality rate of 13%
- Sepsis VDO project launched in 2017
Objectives
Encourage continuous improvement of "Value of Care" through:
- Increasing quality of care while reducing cost
- Minimising variation in care delivered to patients
Methodology
2017
| Conceptualisation of Sepsis VDO (Emergency Department, Department of Medicine, Medical Informatics Team, Finance team), literature review, determined quality indicators and costs to be measured |
|---|
2018
| Cascaded downstream by training of ground teams (simulation sessions)
|
|---|
2019
| Sepsis management concepts and processes implemented and introduced to junior doctors during orientation
|
|---|
2020
| Enhanced "Trigger Programme" initiative
|
|---|
2021
| Reinforcement of key clinical concepts through intensive and remote education efforts; feedback loops with clinical departments |
|---|
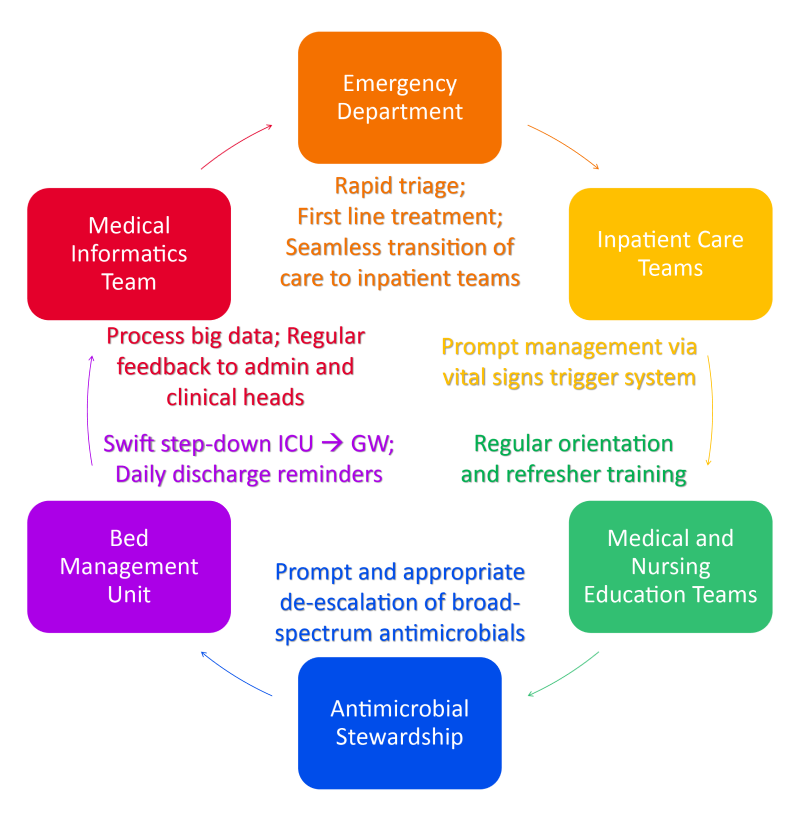
Quality Indicators
- No inpatient mortality
- No emergency readmissions ≤ 30 days (same cause)
- Blood cultures (within 3 hours from triage)
- Antibiotics (within 3 hours from triage)
- Intravenous fluids (within 3 hours from triage)
Results
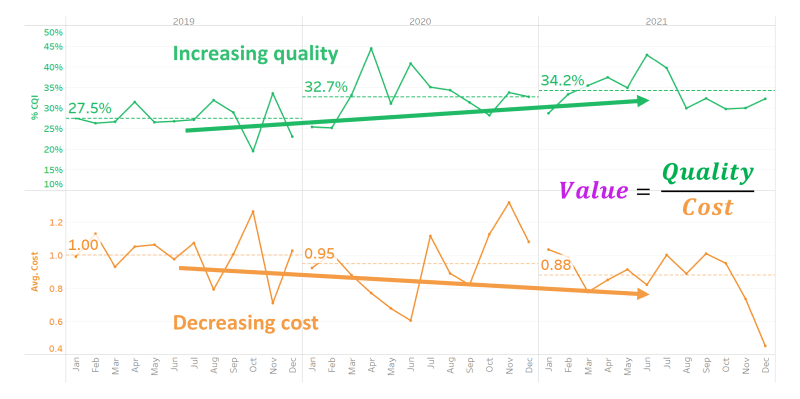
- Increase in Clinical Quality Index (CQI) driven by decreasing cost and increasing quality
- An absolute decrease of 12% points in mean total cost per patient from 2019 to 2021
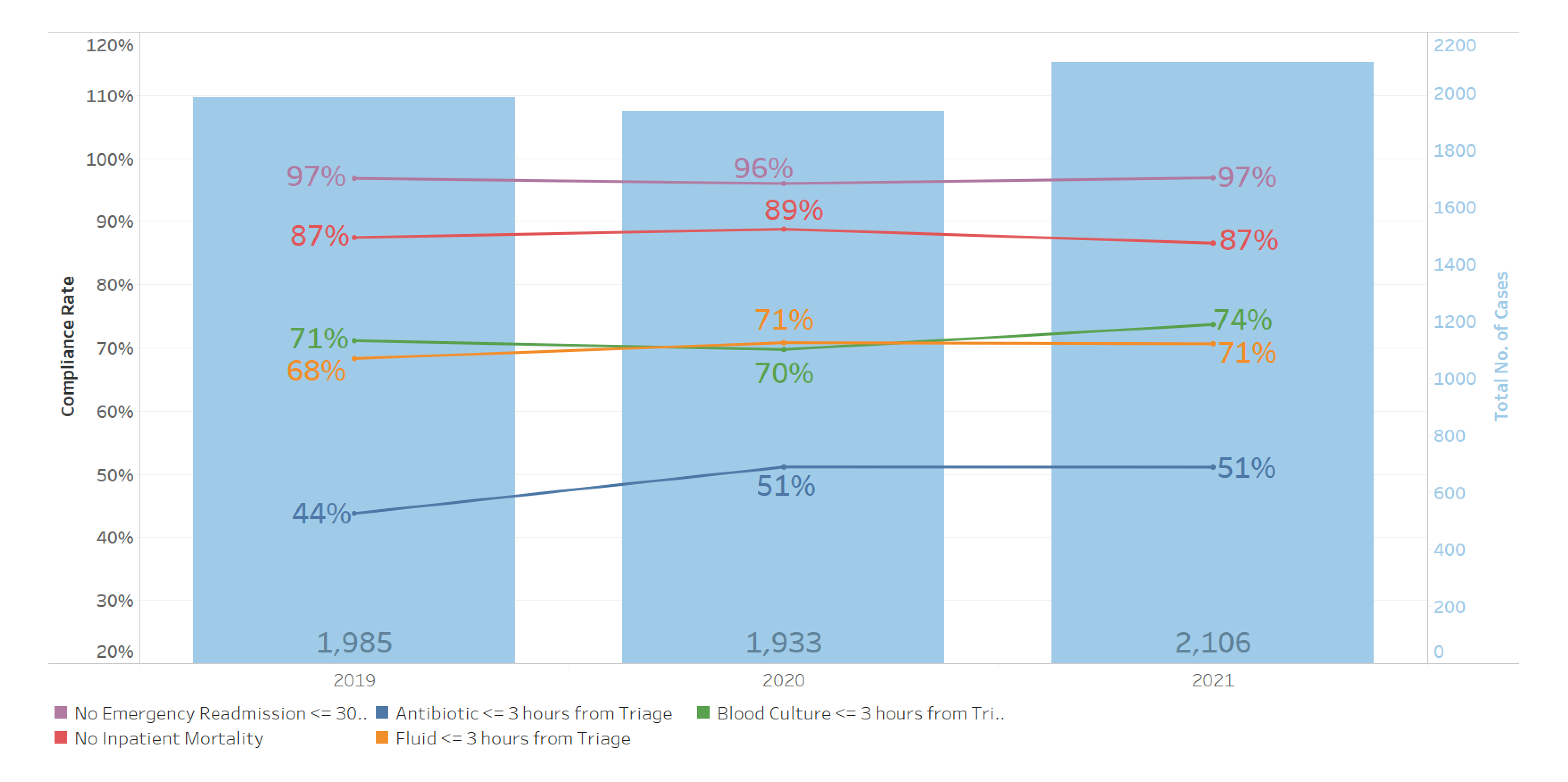
- Antibiotics administration within 3 hours of triage. Increase of 7% to 51% in 2021.
- In 2021, 32% of patients experience Perfect Quality of Care compared to 25% in 2019. (Increase of 7%)
- Rate of appropriate de-escalation of antibiotics. Increase of 1% to 95% in 2021 when compared to 2019
- Average length of stay. Decrease of 3 days from 17 days in 2019 to 14 days in 2021.
- Stable inpatient mortality between 11% and 13% (compares favourably to 18.3% in ANZ)
Conclusion
Improvements in CQI and minimising variation in care achieved and sustained without compromise in mortality, despite challenges posed during COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 and 2021.




















