If you have an acute infection of the lacrimal drainage system, this must be treated with antibiotics. The next step is to determine the degree of obstruction and the site of blockage. This is simply done in the clinic by flushing the tear ducts with saline. Flushing the system might relieve the symptoms temporarily, but they often recur after some time.
Surgery is necessary to treat those with severe obstruction of the tear ducts, or those who have repeated infections of the system. The operation required is called Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR), in which a new channel is created to allow tears to drain into the nose again. Specific operations depend on the site of obstruction.
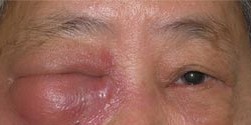
Figure 1 - Severe tear duct infection
Dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR)
DCR is a procedure performed for the treatment of tearing (epiphora) due to blockage of the nasolacrimal duct. It creates an ostium between the tear sac and the nasal cavity by removing the mucosa and bone layers between them.
There are two main approaches to a dacryocystorhinostomy - external and endoscopic. The external approach requires a skin incision. The endoscopic approach creates the ostium from within the nose without the need for a skin incision. Both have similar success rates, with their own advantages and disadvantages.
While external and endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy (DCR) remain the gold standard for nasolacrimal duct obstruction, today we live in a surgical era that strives towards minimally invasive surgery.
Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (NOTES)
NOTES is an emerging field within other disciplines. Lacrimal surgery has seen this trend with the introduction of the microendoscope. Endoscopic lacrimal duct recanalization (ELDR) provides an alternative approach to the treatment of obstructive epiphora. ELDR is currently the least invasive procedure designed for primary acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction (pando). It is appealing as it restores integrity of natural lacrimal drainage system, and avoids the necessity of making new bony openings.


















