Diabetes is a condition where your body is unable to manage blood sugar effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels over time. If left uncontrolled, high blood sugar can lead to complications such as heart disease, eye problems, kidney disease, and other complications.
To improve your blood sugar levels, you can:
- Have a healthy, balanced diet
- Exercise regularly
- Lose weight if you are overweight or obese
What you eat directly impacts your blood sugar levels. However, there is no need to take a special diet for people with diabetes. You do not have to prepare separate meals or buy special ‘diabetic’ foods. Instead, you can follow the Healthy Plate guide for your meals.
Click on the sections below to learn more about carbohydrates, the importance of protein and more.
Healthy Plate Guide
The Healthy Plate guide recommends filling half your plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables for a healthy, well-balanced meal.

Image Credit: National University Polyclinics - 101 Guide to Healthy Eating
What Are Carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates are our bodies’ main source of energy. They are found in many foods and drinks such as fruit, milk, rice, and bread. During digestion, your body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose to provide energy.
However, consuming too much carbohydrates can lead to high blood sugar levels. It is important to know which types of carbohydrates and portions are better for you to prevent your blood sugars from rising too quickly.
Types of Carbohydrates
Starches
- Rice, noodles, bread, biscuits, oats, cereal
- Starchy vegetables like potatoes and sweet potatoes
- Legumes, lentils, and beans
High-fibre starchy foods, such as wholegrains*, beans, and fruit, are digested more slowly. This slows the absorption of glucose into the bloodstream, resulting in a gradual rise in blood sugar levels. Fibre also keeps you full for longer, which helps prevent overeating and weight gain.
*Wholegrain foods include brown rice, wholemeal/multigrain bread, brown rice bee hoon, wholemeal pasta, oats, wholemeal cereals, quinoa, and wholemeal chapatti, among others.
Sugars
- Natural sugars - Found naturally in fruits and dairy products like yoghurt and milk
- Added sugars - Sugar added to food or drinks which include sugars in biscuits, chocolate, sugary drinks, and sweet cereals
Most sugary food and drinks are high in calories and contain few nutrients. Eating too much sugar can lead to weight gain, tooth decay, and poorly controlled blood sugar levels.
You can cut down on added sugars by choosing:
- Plain water or beverages that do not contain sugar
- Fresh fruit instead of fruit juice or dried fruit.
A Dietitian's Tip
Beware of food and drinks with “no added sugar” as they may contain natural sugars and raise blood sugar levels.
Hidden sugars can come in many forms and are often hidden in many food products such as:
- Honey
- High fructose corn syrup
- Brown sugar
- Fructose
- Lactose
- Gula Melaka
- Molasse
- Sucrose
- Dextrose
- Maltose
The Importance of Protein
Protein is an important part of a balanced diet, especially for people with diabetes.
- Protein digestion and absorption is slower compared to carbohydrates, so it does not spike blood sugar. Including protein in your meal will also slow down the absorption of sugar into the blood stream.
- Protein foods keep you feeling full and satisfied longer compared to fats or carbs. This prolonged feeling of fullness can prevent overeating and promote weight management.
- Protein is essential for building and maintaining muscle mass. People with diabetes often lose muscle mass, so eating enough protein helps preserve lean body mass.
Good sources of protein include lean meats like chicken, fish, eggs, beans, lentils, nuts, seeds, and low-fat dairy products like low-fat milk, Greek yoghurt, and cottage cheese. Aim to include some protein in your meals and snacks to help stabilise blood sugar levels. Some examples are:
- Nut butter or cheese with wholegrain bread
- Oats with reduced sugar soymilk or low-fat milk
- Fish, tofu or lean meat with main meals
- Beans or lentils in salads
Reduce Fat and Salt
People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing high cholesterol and heart disease. Reducing overall fat and salt in the diet can help lower this risk.
Healthier choices
| Choose less of these
|
|---|
- Fish
- Tofu
- Lean meat
- Chicken/duck/turkey without skin
| - Meat with visible fats
- Poultry skin
- Organ meats
- Processed meats e.g. sausages, ham
- Deep fried foods
|
Cooking oil and margarine with the healthier choice symbol  | - Butter, lard, ghee
- Coconut oil, palm oil, blended vegetable oil
- Coconut milk and its products
|
| Healthier cooking methods such as steam, broil, soup, stew, bake, grill | Deep-fried items and snacks
(not more than twice a week) |
| Low fat dairy products | Full cream dairy products |
- Fresh ingredients, herbs and spices, onion, garlic, ginger, chilli
- Reduced salt products
| - Preserved or salted foods
- Seasonings, condiments, or seasoning powder
- Foods with added salt/pre-packaged seasoning
- Stock powder/stock cubes
|
Building Balanced Meals – Tips for Creating a Healthy Plate
Hear are some tips on how to make your plate healthier:
- Have more vegetables
- Ask for less gravy
- Avoid adding ketchup or soya sauce
Sample Meals
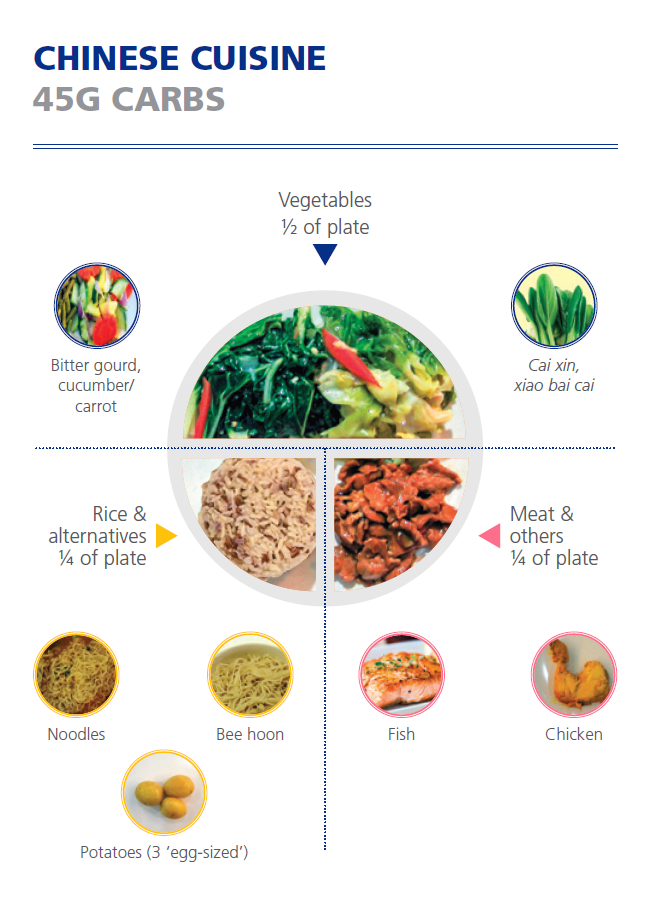
Chinese cuisine
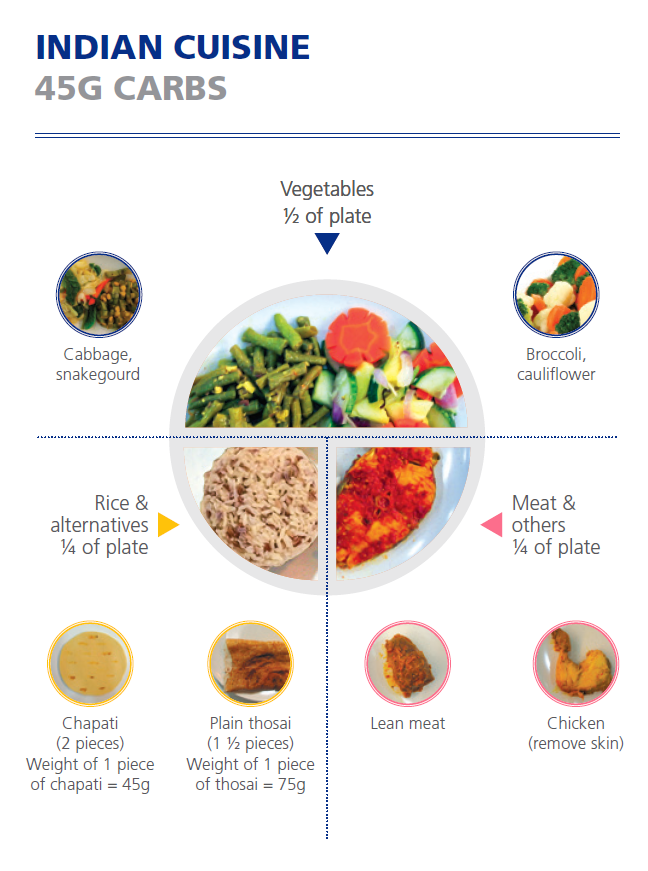
Indian cuisine 
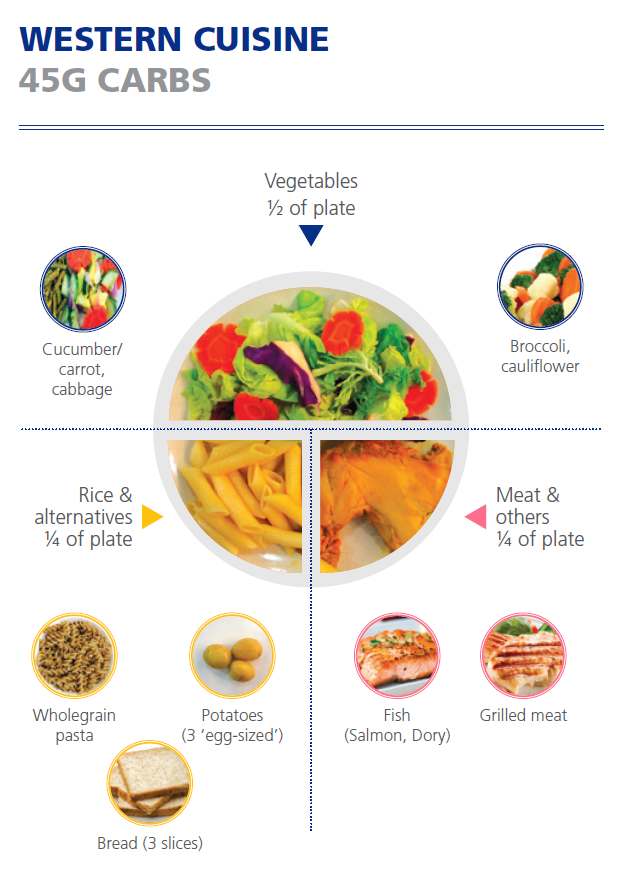
| Western cuisine 
|
Other sample meals
Sample meal plan
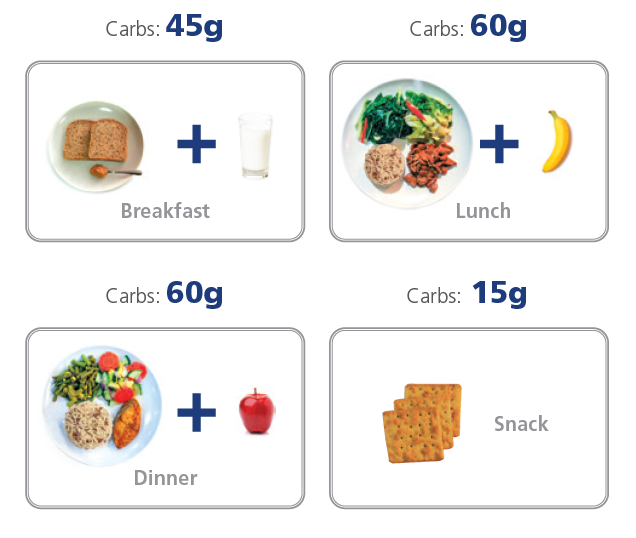
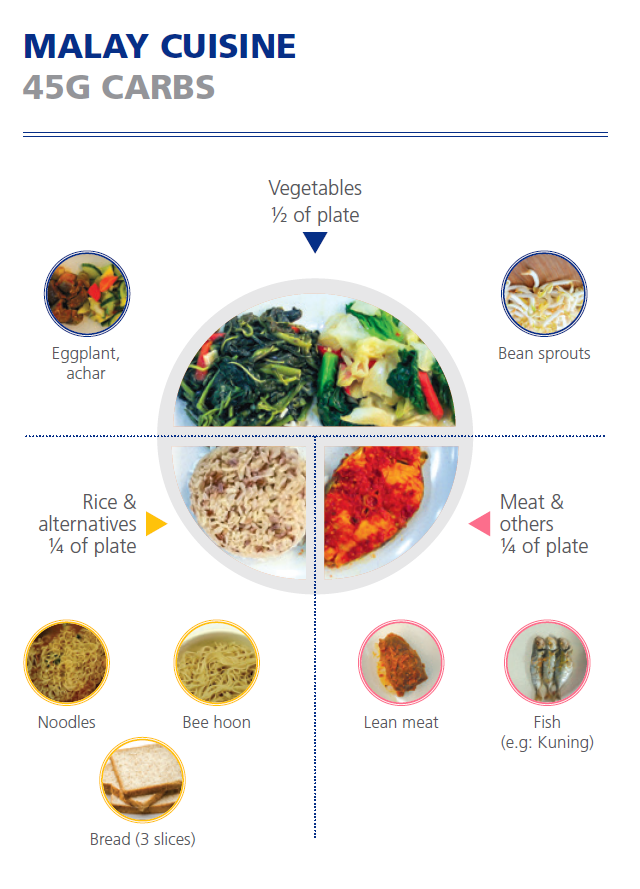
Figures from HealthHub and National University Polyclinics' Carbohydrate Counting Booklet
Smart Snacking
When you have diabetes, it is important to choose snacks wisely to help control blood sugar levels. Some healthy snacking options include:
- One serving of fresh fruit like apples, berries, or citrus fruits. These provide fibre, vitamins, and antioxidants without spiking blood sugar.
- 10 pieces of nuts like almonds, walnuts, or pecans. These are high in healthy fats and protein, which are better for blood sugar levels. Avoid flavoured or salted nuts, as they can be high in fat and sodium.
- 1 to 2 tablespoons of nut butter with celery sticks or wholegrain bread.
- 1 slice of cheese with 1 slice of wholegrain bread.
- 1 glass of low-fat milk or soymilk.
The key is to limit high-sugar and high-carbohydates' snacks. Focus instead on options that are rich in fibre, protein, and healthy fats.
Diabetes Myths and Facts
Myth 1: I have type 2 diabetes because I ate too much sugary food and carbohydrates
Family history, older age, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. While sugar alone does not directly cause diabetes, consuming a high-calorie diet coupled with low physical activity can promote weight gain and obesity, which significantly raise one's risk.
Myth 2: People with diabetes should avoid carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are an important source of energy and nutrients. However, they can also raise blood sugar levels. Instead of avoiding carbohydrates, focus on controlling the amount and types of carbohydrates you eat to help manage your blood sugar levels.
Myth 3: Skipping meals will help to control my diabetes
Skipping meals can lead to spikes and drops in your blood sugar. When you skip meals, your blood sugar can fall too low, making you feel very hungry. This hunger may cause you to overeat at your next meal, resulting in a blood sugar spike. To help manage your diabetes, it's important to eat regular, balanced meals throughout the day.
Five Tips to Help Manage Blood Sugar Levels
- Eat Regular Meals: Eating at consistent times throughout the day helps keep your blood sugar steady, preventing spikes and drops.
- Control Carbohydrate Portions: Large amounts of carbohydrates can cause rapid increases in blood sugar levels. Monitor your portions to maintain better control.
- Limit Added Sugars and Refined Carbohydrates: Foods like sweets, soft drinks, and desserts can cause quick rises in blood sugar. Opt for alternatives with less or no added sugar.
- Choose Healthier Fats: Consume less unhealthy fats such as saturated and trans fats found in fatty meats, butter, and fried foods. Instead, add healthy fats like olive oil, avocados, and fish to your diet to help prevent weight gain, lower cholesterol, and improve blood sugar control.
- Eat More Foods High in Fibre: Fibre helps control blood sugar by slowing down digestion. Good sources of fibre include fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can intermittent fasting (IF) help with weight loss?
Intermittent fasting is a popular eating pattern that has different methods. The most common is called ‘time-restricted eating’, where you eat only during specific hours and fast for the rest of the day.
By limiting eating hours, most people will eat fewer meals, which can help with weight loss. However, sticking to this routine can be challenging, and some may experience side effects such as headaches, dizziness, or fatigue.
For individuals with diabetes, intermittent fasting requires extra caution. It is essential to closely monitor blood sugar levels while fasting. Going for prolonged periods without food can cause low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia), especially if you are taking medications that increase this risk.
If you have diabetes, you need to be extra careful with intermittent fasting. It is important to keep a monitor your blood sugar levels closely while fasting. Going on long periods without food can make your blood sugar become too low especially if you are on diabetes medications that can cause low blood sugar.
When breaking your fast, aim for healthy, balanced meals. Avoid overeating during eating hours, as this could lead to excessive caloric intake.
Before starting intermittent fasting, consult your doctor and dietitian. They can assess whether this approach is safe for you, especially if you are on medications or have other health concerns.
- Should I use nutrition supplements made for people with diabetes?
Nutrition supplements for people with diabetes usually come in the form of drinks or snacks that are designed to cause a slower rise in blood sugar levels compared to regular foods.
These supplements can be used in various ways:
- As a meal replacement: If you are managing your weight, they can replace a regular meal due to their lower calorie content.
- To provide extra nutrition: If you are not eating well, these can help provide essential nutrients that your body needs.
- As a snack: They can be consumed between meals when you need a convenient option.
It is important to note that while these supplements are designed for people with diabetes, they are not intended to control blood sugar levels on their own. These supplements still contain calories and carbohydrates, and consuming them in addition to your regular meals could lead to weight gain, or elevated blood sugar levels.
Always consult your doctor or dietitian before adding these supplements into your diet. They can help determine whether you need them and how to use them effectively as part of your overall diabetes management plan.
Additional Resources
Back to 'Managing Diabetes' >